Overview:
As of January 2021, the free version of Redhat, namely CentOS 8 has been marked as being discontinued with the date of December 2021. Therefore, Ubuntu Server 20 and Fedora Server 33 are being favored by many organizations as freeware in lieu CentOS. This article is an illustration of the installation process of Ubuntu.
Step 1:
- Download the latest version from Ubuntu Server from https://ubuntu.com/download/server
- Create a bootable USB thumb drive or burn ISO image onto a DVD
Step 2:
- Bootup a computer using the ISO installation referenced previously > Continue > Continue without updating > Accept language and keyboard defaults > Done
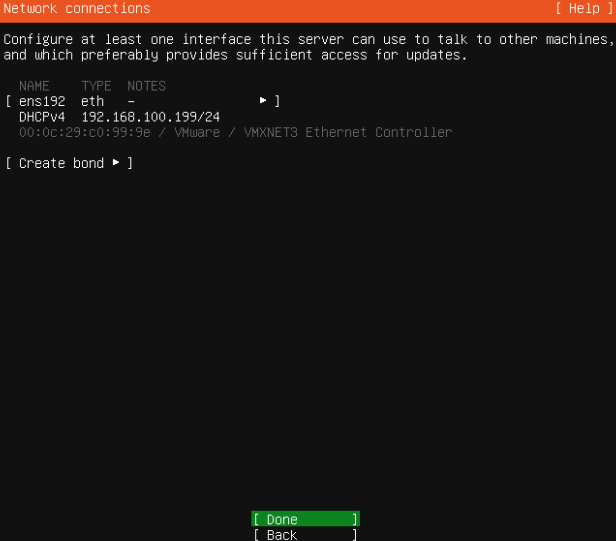
- Configure network connections, if necessary > Done
- Configure proxy, if necessary > Done > Done
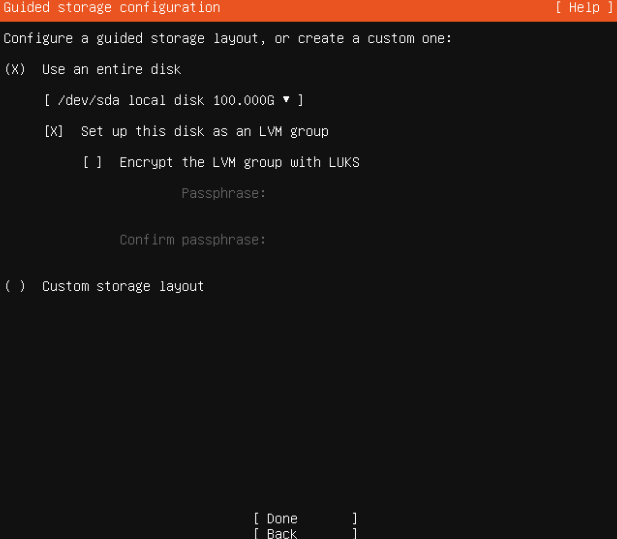
- Use an entire disk > Set up this disk as an LVM group (recommended for ease of administration) > Done
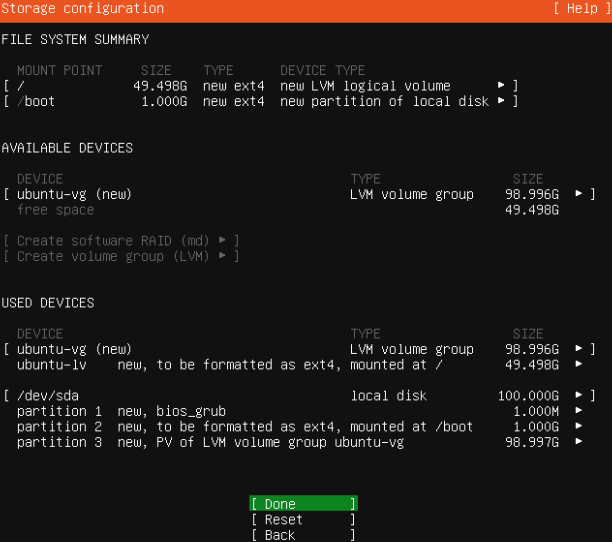
- Review the File System Summary > Done
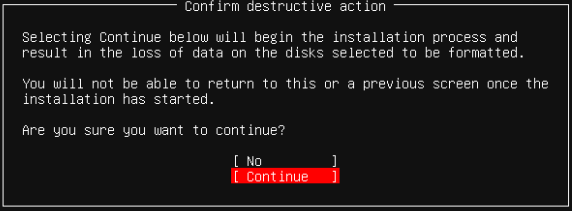
- Confirm destructive action warning to wipe the disks and begin installation > select Continue
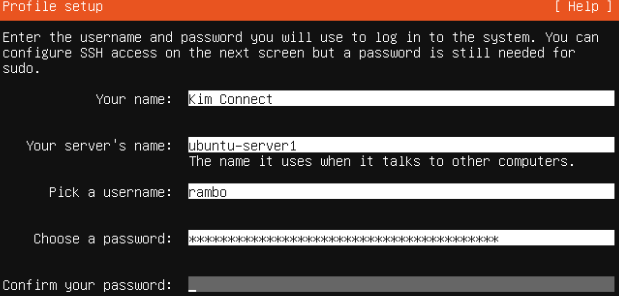
- Input profile setup information > Done
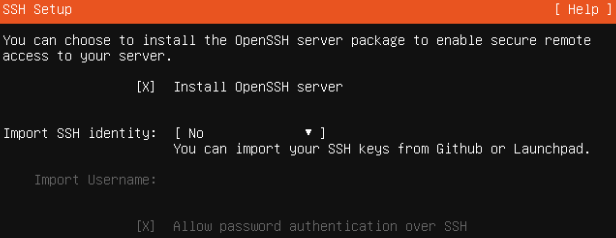
- Press space bar to select Install OpenSSH server > Done
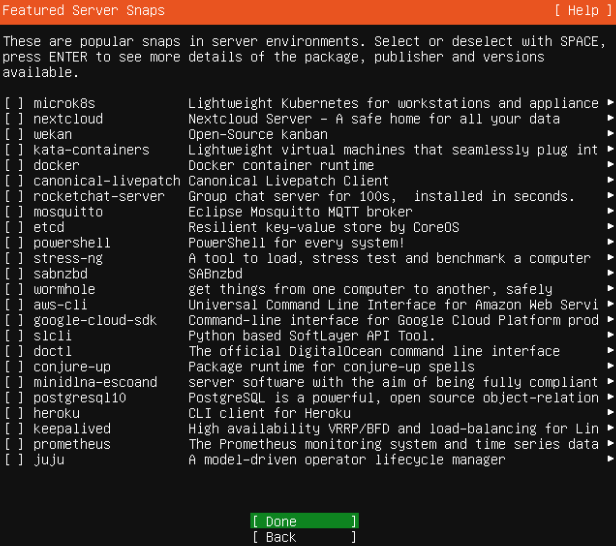
- Select any Featured Server Snaps repositories as required > Done
- Wait for the installation process to complete > be advised that the ‘downloading and installing security updates’ may take awhile > reboot machine when the OS has finished installing
Step 3: Configure Networking
# Check for network interfaces
root@ubuntu-server:/home/rambo# ip link
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
2: ens160: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP mode DEFAULT group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:0c:29:20:47:32 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
# Configure networking
sudo vi /etc/netplan/*.yaml
### Sample content ###
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens160:
dhcp4: false
addresses: [10.10.10.99/24]
gateway4: 10.10.10.1
nameservers:
addresses: [8.8.8.8,1.1.1.1]
#######################
# Apply new network configuration
sudo netplan apply
Step 4: Set Server Host Name
# Change the hostname
hostname=linux01
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname $hostname
# Notice the output that the new hostname doesn't update shell prompt immediately
root@ubuntu-server1:/home/rambo# sudo hostnamectl set-hostname $hostname
# Update the /etc/hosts file
sed -i '/127.0.1.1/ c\127.0.1.1 '"$hostname"'' /etc/hosts
# Update cloud.cfg
sed -i '/preserve_hostname:/ c\preserve_hostname: true' /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
# verify that new hostname has been successfully set
root@ubuntu-server1:/home/rambo# hostnamectl
Static hostname: linux01
Icon name: computer-vm
Chassis: vm
Machine ID: f377574c9e954e139ac21f16422aba49
Boot ID: 19e1c774e9e842539dbb8269ed65858b
Virtualization: vmware
Operating System: Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS
Kernel: Linux 5.4.0-62-generic
Architecture: x86-64
# Restart the machine for changes to be reloaded
sudo reboot
Step 5: Change The GRUB 2 Default Timeout
# Edit the grub file
sudo vim /etc/default/grub
########### Sample values ###########
GRUB_DEFAULT=1 # Set this as non-zero
GRUB_TIMEOUT_STYLE=hidden
GRUB_TIMEOUT=1 # Change this as well
GRUB_DISTRIBUTOR=`lsb_release -i -s 2> /dev/null || echo Debian`
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT=""
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX=""
# Save the file and update
sudo update-grub
Step 6: Configure Automatic Updates
sudo apt install unattended-upgrades -y
sudo dpkg-reconfigure --priority=low unattended-upgrades
Categories: