Overview:
Internet Service Providers would terminate their wiring at the customer premise equipments (CPE) as a Internet modems. From there, it’s up to the users to setup their network to suite their purposes. In this short article, we shall be observing a cogent design of a small network with emphasis on strong wireless fidelity (WiFi).
Network Topology:
Certain modems would be a combination unit that has wireless capabilities. If so, such Wifi functions should be disabled in favor of a more robust schema. Hence, a single Ethernet cable would be used to connect such modem with a non-wireless router. In this illustration, we’re using a router with virtual lan (VLAN) capability. There shall be two VLANs to separate the ‘private’ (VLAN ID 1) network with a ‘guests’ network (VLAN ID 101). Although its conceivable that a downstream networking switch could further seggregating traffic by port numbers, that complication is beyond the scope of this illustration.
(1) Internet Modem (Motorola) <==> (2) Firewall (SonicWall) <==> (3) Gigabit Switch (Linksys)
The switching apparatus would be connecting directly toward computer desktops/laptops to eliminate the requirement for wifi. However, that is no longer a practical solution as many home devices such as smart phones, tablets, tv boxes, surveilance cameras, and appliances are connecting via wireless nowadays. Therefore, it’s necessary to construct this service using modestly costed Ubiquiti solutions. Herein, we would be running a ‘Unifi Controller’ software on a virtual server to control wireless access points and range extenders.
Gigabit Switch:
<=> Mini Server with VmWare
<=> Unifi Controller (Ubuntu Server with Unifi Controller App)
<=> Uniquiti Access Point (UAP-AC-Pro)
<=> Ubiquiti Wifi Extender (UAP-BeaconHD)
High-level view of tasks:
1. Connect modem to router
2. Connect router to switch(es)
3. Connect switch(es) to Wireless AP and Virtual Server
4. Connect Wireless Access Point
5. Connect Wireless Range Extender
6. Install Linux (Ubuntu) OS onto server
7. Install Wireless Controller Application on a server
8. Configure router to create 2 VLANs
9. Configure Wireless Controller
Some quick instructions:
How to Add VLANs to Sonicwall
Authenticate into Firewall > Navigate to Network > Interfaces > click Add Interface > Input values for Zone, VLAN Tag, Parent Interface, Mode, IP Address, Subnet Mask
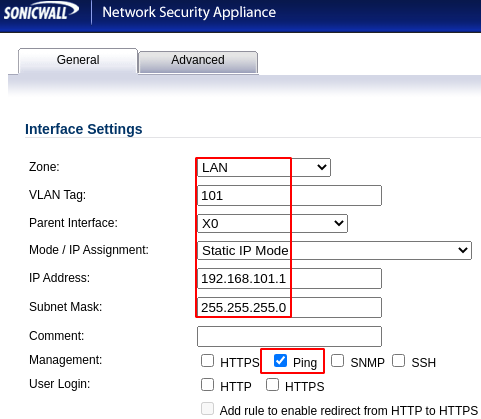
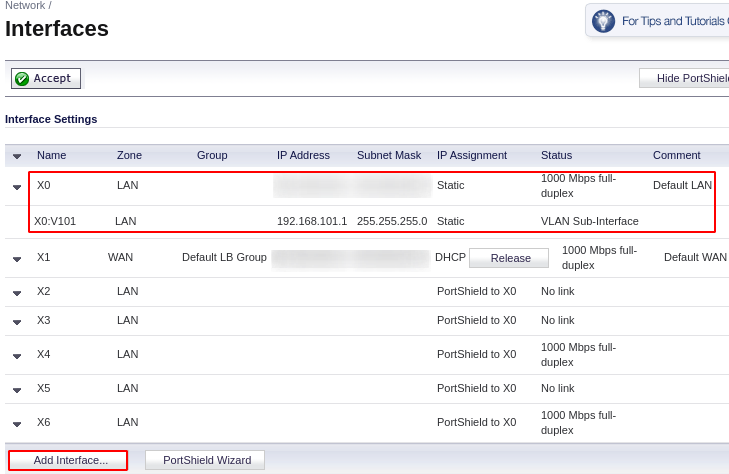
Repeat adding interface for each new VLAN
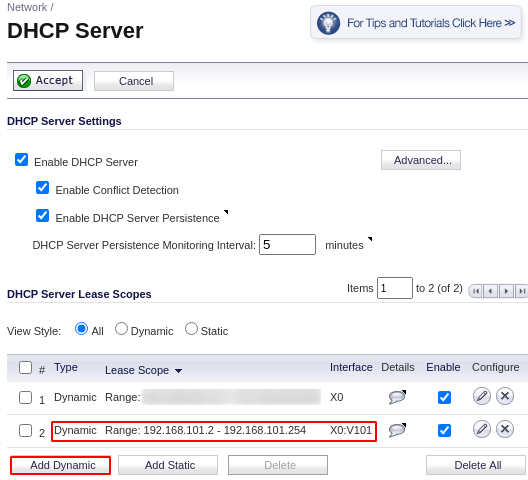
Navigate to Network > DHCP Server > click Add Dynamic > Input values to create two DHCP ranges shown below
How to Configure Unifi Controller
Installation of this software is detailed in this blog.
To ‘adopt’ wireless access points (AP’s), Authenticate to Unifi Controller > Navigate to Devices > click on any device that has the ‘adopt’ link highlighted (if any) > wait for the process to complete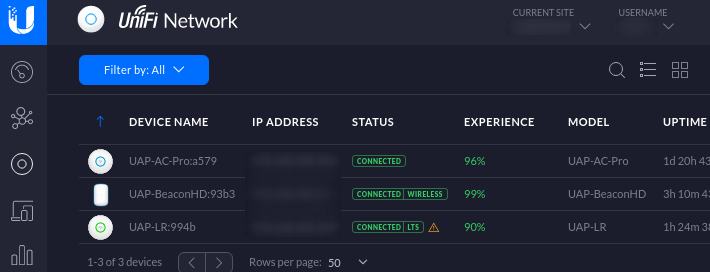
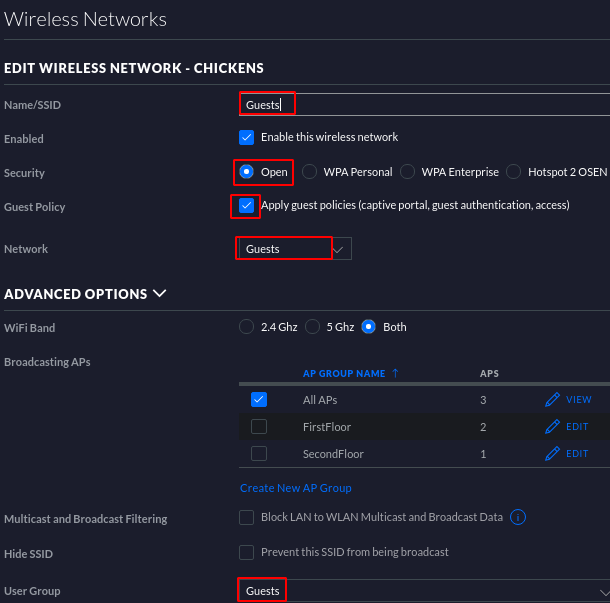
To create a Guests network, navigate to Settings > Networks > Create New Network > input values as illustrated below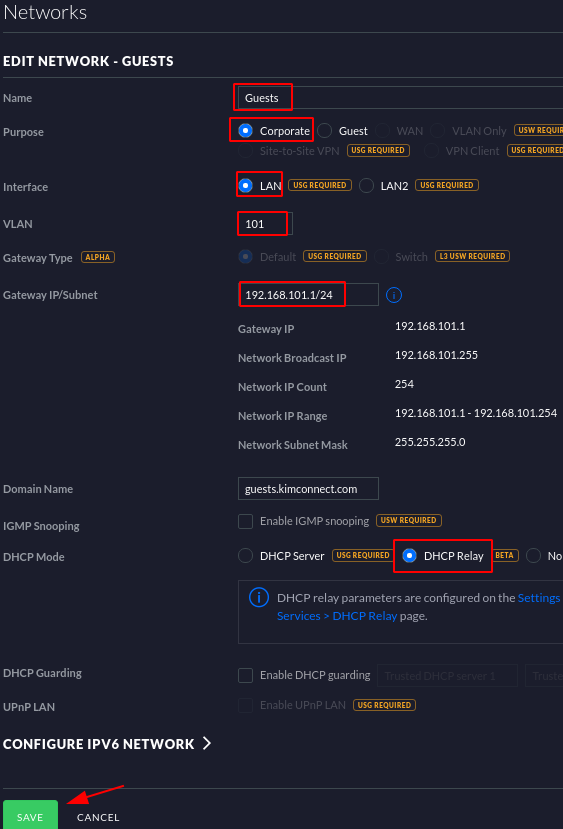
Navigate to > click on DHCP > Add > input the IP address of the VLAN gateway virtual interface as created in prior instructions > Save when ready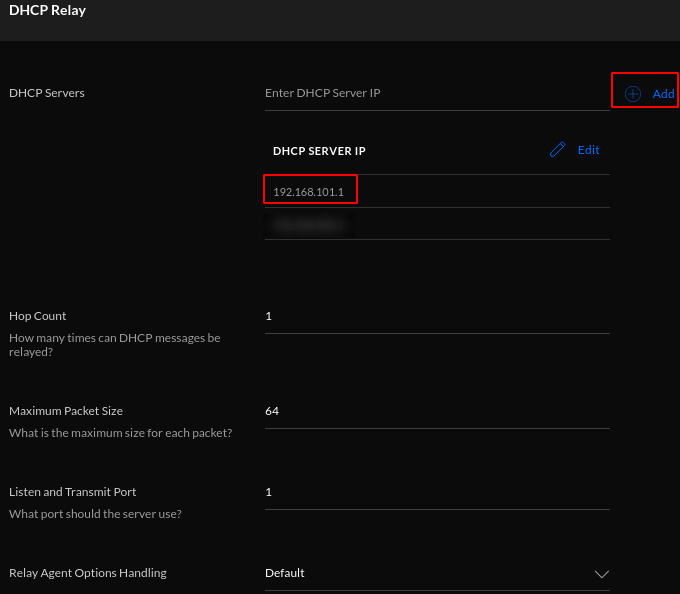
Navigate to User Groups > Create New User Group > Input values shown below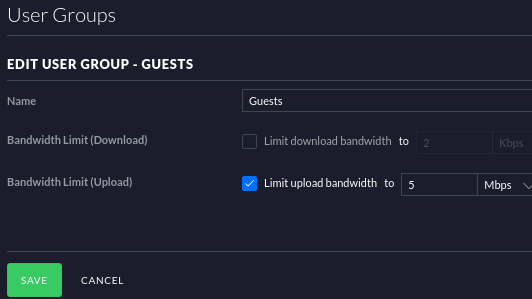
Navigate to Wireless Networks > Create New Wireless Network > Input values similar to these > click Save when done > click Devices to observe provisioning progress of new settings to all connected AP’s